Diamond Prices
Read moreDiamond Resources
FAQ – Diamond Education – Resources about diamonds
Comprehensive, easy to follow diamond glossary and guides on diamond buying.
Discover all the essentials you will need to buy diamonds – avoid dirty tips and tricks
Diamonds: Frequently Asked Questions
Why is there such a big difference in cheap priced diamonds by online sellers and Ajediam?
4C’s in fact 8C’s Essential knowledge about diamonds.
Alluvial diamonds: In riverbeds, diamonds are harvested by sorting and washing the dug, pumped, or dredged river gravel (alluvial mining).
Exploitation of sandy coastal strata is done by open terrace construction (marine mining).
Baguette is always rectangular and has alternating facets, which makes it a favourite ring stone.
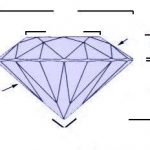
Brilliant cut is round with its 57 facets and minimum loss in cutting, the classic and most popular modern brilliant cut.
Cachet: When a broker handles transactions, and an agreement has been reached with the buyer, the parcel is sealed by putting it in an envelope with the signature of the buyer and the price per carat on it. A sealed lot is a cachet. A cachet with a price remains valid until the closing hour of the trade room the following workday.
Certificates Department (HRD) [Co-operates closely with the Antwerp University. The department draws up diamond certificates in a scientific way. These certificates describe the quality and the characteristics of a diamond as accurately as possible.]
Clarity – or purity – of a diamond is determined by the number, the size, the brightness and the location of the internal and external characteristics, important structure phenomena and transparency.
Clarity Best grade is called loupe clean, literally meaning clean when viewed through a loupe.
Clarity lowest grade on the scale (indicated by P for Piqué) refer to inclusions that can be seen by an experienced grader with the naked eye. Depending on the importance of the characteristics, P1, P2 and P3 are distinguished.
Color Best is called “exceptional white+”; the lowest colour on the scale is called “tinted colour”. Between brackets, the colour grade is given according to an alphabetic scale ranging from D, the best colour, to S-Z.
Color of a diamond is determined by comparing it to an internationally approved series of master stones.
Cutting process:
Cutting study: Marking: Each diamond is unique. Each stone must therefore be studied in detail in order to determine the most advantageous manner to work it with the least loss of weight and the greatest clarity. With a pen and India ink, the direction in which the diamond must be Cleave: cleaved or sawn is indicated.
cut a rough stone, it is first set in quick drying cement on a wooden holder or dop. With another, sharp diamond placed on a smaller wooden dop, a groove is made. Then a steel wedge with a rounded edge is placed in the groove. A sharp blow with a mallet on this blade splits the stone. Cleaving is done parallel with the grain of the crystal.
Faceting: A diamond is faceted on a polishing wheel. This machine consists of a horizontal, circular cast-iron disc that is, of course, charged with diamond dust. The cut stone is clamped in an adjustable dop, which is set at a particular angle, and with the aid of clamps pressed against the disc. This process is called gross work. Both on the crown (the part above the girdle, i.e. the plane with the greatest diameter) as on the pavilion (the part under the girdle), 4 facets are first placed. The rest of the facets are placed on the ribs of the preceding facets by resetting the dop. In total, a brilliant has 57 facets: the table (the large central facet), 32 facets on the crown, and 24 facets on the pavilion. The facet form is, of course, dependent on the size and the form of the rough diamond.
Diamond High Council (HRD) is a non-profit organisation at the service of the Belgian diamond trade and industry
Diamond is the hardest mineral known to man – its hardness coefficient is 10 on the Mohs scale.
Diamond Office (HRD) regulates importation and exportation as well as the customs formalities and the organisation of safe, rapid shipment
Parcel: Diamonds are kept in lots, named parcels
Emerald shape is a refined variant of the baguette with a famous jewel tradition.
Fancy colors Are colored diamonds. The most beautiful are pink and purplish pink
Finish grade testifies of the workmanship of the diamond polisher.
Fluorescence is determined by comparing the diamond to a series of master stones – special test stones indicating the limits between the different grades – under long-wave UV-light. The fluorescence grades are: nil, slight, medium and strong.
Fluorescence is the effect whereby invisible ultraviolet light is transformed into visible light. Some stones light up spectacularly in the dark when irradiated by long-wave ultraviolet light.
Gemmological Institute (HRD) Gives courses and seminars on international level on gemmology and on the certification of diamonds.
Girdling is the second step in the process of cutting, which was already known in Renaissance times. This is the rounding of the base of the sawn (or cleaved) piece so that it has more or less the form of a polished diamond. To do this, the sawn diamond, again in a dop, is mounted on the chuck of a lathe. The desired rounded form is achieved by turning it against another diamond mounted on a long wooden dop. The diamond dust that is created, is carefully collected in a small reservoir.
Heart shape has, of course, a high emotional value and is thus popular as engagement diamond.
Inclusions = impurities inside the stone.
Loupe clean is followed by the clarity grades vvs1 / vvs2, which stand for very very small characteristics, very hard to find with the loupe. The next grades, in descending order, are vs1/vs2 (very small characteristics) and si1/si2 (small inclusions).
Marquise or navette, which issues in a point above and below, can be broader or narrower depending on its application in the design of the jewel.
Mazal: Professionals buy and sell according to the traditional rules. A handshake and the words “Mazal U’ Bracha” are sufficient to make a deal.
Measurements of a diamond are expressed in millimetres.
Oval shape is modified brilliant cut. Popular variant of the classic round form in diamond jewellery.
Pear shape or tear drop is the name of this form. The Star of South Africa has this pear shaped form, which is often used in pendants.
Proportions is the relationship between the various parts of the stone, determine the fire and brilliance of the diamond. If the proportions are not optimal, undesirable visual effects may occur.
Rough, uncut diamonds: In its unpolished form, a diamond is a rather vague crystal form, without any real lustre. Only a succession of processes gives it its final facet form and brilliance.
Sawing, the diamond is divided against the grain. Before a diamond is sawn, it is secured: the marked stone is set in a copper dop with a paste consisting of a mixture of plaster and glue. After a specific baking time in which the paste is hardened, the dop is mounted on the saw. The diamond is set against a high speed (15,000 rpm) vertical blade and sawn very slowly. The extremely thin saw blade, which is made of phosphor bronze, is coated with diamond powder mixed with oil. The sawing of a large stone can sometimes take days or weeks. A new technique of sawing diamonds with laser beams was developed.
Scientific and Technical Research Center (WTOCD). Studies the existing production methods and strives, with the aid of new techniques, to increase productivity and improve quality.
Sealed diamonds: the diamond can be sealed in a tranparent holder together with a microfilm of the certificate. Not only does the sealing keep the diamond safe from damage, grease and dirt, it is also a guarantee that a given certificate and the accompanying stone actually belong together.
Symmetry – deviations and the proportions are first judged based on objective, measured data. For this purpose, a Dia-Mension system is used: with the aid of a camera a large number of measurements are taken, after which these are interpreted by a computer.
Glossary:
One minute diamond course for free
4 C’s:
Carat size:
Ring size chart
Shapes:
Color diamonds:
Color tinted diamonds grading chart
Understand Diamond Certificates:
Diamond certificate + diamond image
No blood diamonds, conflict diamonds
Investing in diamonds:
Wholesale diamond prices:
Colored – tinted diamonds – prices
Rapaport | Diamond Trade Prices
http://www.diamonds.net/Info/AboutRDR.aspx
Treated diamonds:
Fake diamonds, simulants – Test diamonds
When diamonds were formed + how
Mysterious natural rough diamonds
Famous diamonds, mines, places:
The biggest diamonds and the
biggest diamond mines in the world
How to visit Antwerp – quick guide
Jewelry care:
Precious metals, jewelry care for diamonds, pearls and settings
Discover World’s most luxury
Famous Jewelry Houses legendary
Fashion Designers and famous
Avoid Dirty Tricks!
Get your free copy of
Useful tips on diamonds buying